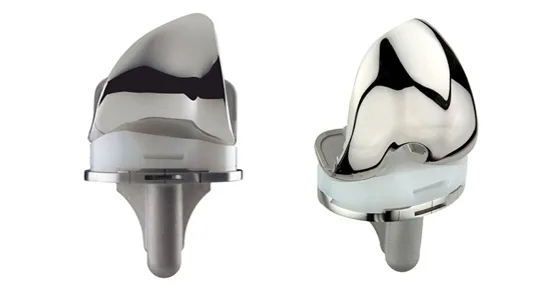
Il sistema di protesi di ginocchio a pivot mediale Advance® è stato introdotto per la prima volta sul mercato nel 1998. Le evidenze prodotte in anni di ricerca e progettazione da parte di Wright Medical e del Dr. J. David Blaha hanno portato ad un design innovativo per gli interventi di artroplastica di ginocchio.
Il design esclusivo del sistema di protesi di ginocchio a pivot mediale Advance® consente di riprodurre al meglio la stabilità e il movimento di un ginocchio nativo. Grazie alla stabilità del comparto mediale e alla mobilità di quello laterale, il sistema a pivot mediale Advance® è progettato per simulare la sensazione e la funzionalità di un ginocchio naturale.